What Is The Difference Between A Core System And A Business System And The Relationship With ERP?
IT systems are crucial for promoting safe, reliable, and efficient corporate management. Introducing a suitable system can significantly improve competitiveness, enhance customer trust, and reduce employee work hours and human errors.
However, the existence of multiple types of IT systems, such as “core system,” “business system,” and “ERP,” often leads to confusion. Understanding the role of each can be challenging.
In this explanation, I will detail the differences between core systems, business systems, and their relationship with ERP.
What is the Core System?
A “core system” refers to a critical IT system that manages the core business operations, serving as the foundation of a company’s overall functioning. The specific core operations can vary depending on the industry, business type, and the organization itself. However, they typically include functions such as production management, sales management, and financial accounting management.
What distinguishes core systems is their crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of essential business processes. If any malfunction occurs in these core systems, it can lead to immediate and severe damage to the company’s management and overall performance.
For instance, in the manufacturing industry, “production control” is a vital lifeline. The ability to track which products will be produced, where and when, as well as managing personnel assignments and rotations, is essential for the company’s existence and stability.
Similarly, in the logistics industry, the core system’s functionality in managing warehouse flows, such as warehousing, inventory, inspection, packing, shipping, and arranging delivery trucks, is critical. Failure in this area can result in significant damage to business partners, customers, and related companies, leading to a loss of credibility.
The key characteristic of core systems is their integration of multiple functions that used to be performed separately. By bringing these operations together, core systems can significantly improve operational efficiency, standardization, labor savings, and cost reduction within the organization.
In summary, core systems are the backbone of a company’s IT infrastructure, managing essential business processes. Their proper functioning is crucial for the company’s success, while their integration and efficiency contribute to overall business improvements.
There are 6 types of main core systems.
- Inventory management system
- Purchasing management system
- Sales management system
- Production management system
- Accounting management system
- HR payroll system
Let’s take a quick look at each.
Read more: [2023] Top 10 recommended system development outsourcing companies in Vietnam
| Inventory Management System | This system grasps the inventory quantity and location (storage location) of each product and manages appropriate inventory by integrating it with incoming/outgoing information. In order to maintain proper inventory, there is also a function to notify you with an alert if there is an excess or deficiency in inventory. |
| Purchasing Management System | It manages and inspects the ordering and purchasing of products and raw materials, and cooperates with the inventory system. Some also have features for estimating and billing. |
| Sales Management System | In sales, this system manages the flow of money, such as quotations, sales, invoices, deposits, and payments, and the flow of products, such as ordering, purchasing, shipping, and inventory. |
| Production Management System | In order to efficiently manufacture with the shortest lead time, we perform production planning, ordering, worker management and work instructions, progress management, cost management, etc. |
| Accounting Management System | It automates the creation of the general ledger, income statement, and balance sheet, starting with daily journal entries in accounting operations. If you can understand the basic operations, you can streamline your accounting work without any special knowledge. |
| HR Payroll System | This is a system that unifies personnel management, which manages basic employee information and information related to careers and skills, and payroll management, such as payroll calculation, payment, and payslip management. By integrating the two, it is possible to promote the accuracy and efficiency of personnel assessment and payroll operations. |
What is a Business System?
“Business system” is often used together with the core system. The major difference from mission-critical systems is that even if there is a problem with the function for some reason, it does not directly affect the core operations of the company.
In other words, business systems are designed to improve the efficiency of specific operations, save labor, and reduce costs within particular areas or departments of the organization. They are typically targeted at streamlining processes and enhancing productivity in a focused manner.
Type of Business System
Depending on the industry or type of business, some companies opt to develop their own system to support special operations unique to their organization. This type of system is also known as a business system. Examples of Business Systems include:
- Purchasing management system
- Attendance management system
- Quotation management system
- Quality control system
- Customer management system
Business System Usage Example
Let’s take a closer look at a business system use case.
The Attendance Management System’s primary purpose is to manage employee attendance and track working hours for payroll calculation accurately. This involves capturing data on ‘when,’ ‘where,’ ‘who,’ and ‘how long’ employees are working.
Traditionally, many workplaces use manual methods like printing time cards on paper and collecting them with the responsible person. This process requires additional effort to calculate working hours, overtime, and other payroll-related figures for each employee. It becomes more complex when employees work at multiple branches or stores, requiring frequent check-ins and check-outs from various locations. This can lead to significant time and effort expenditure and poses a risk of human error.
By implementing an attendance management system, companies can manage the attendance of all employees in real time, irrespective of their location or work hours. Additionally, the system can automatically record the required data for payroll calculation, including irregular patterns like overtime, late-night work, and holiday shifts. This automation significantly improves work efficiency and reduces the chances of errors, leading to a more streamlined and standardized process.
“Purchase management system”
“In the manufacturing industry, efficient procurement of raw materials at lower prices, in larger quantities, and at optimal times is crucial for improving operational efficiency and reducing costs. Similarly, in non-manufacturing industries, cost-effective procurement of products and equipment is essential for promoting lean management.
One challenge arises when different departments and personnel handle procurement separately, leading to difficulty in tracking past purchase history. This can result in errors such as buying the same material from different suppliers, placing duplicate orders, and purchasing at varying prices. Such practices may lead to excessive costs and hinder building strong relationships with business partners. Each person in charge may adopt ad hoc procurement methods, resulting in significant losses.
Implementing a purchasing management system allows the sharing and utilization of consistent information across multiple departments and personnel. This ensures that high-quality materials and products are procured at the right cost and at the appropriate time, eliminating concerns about excess or shortage of inventory.
By adopting a purchasing management system, companies can streamline procurement processes, make well-informed decisions, and achieve cost savings, ultimately contributing to overall operational efficiency and successful inventory management.
“Customer management system”
In order to build good relationships with customers and have them continue to use our products and services, it has become common practice to use communication tools via the Internet, such as SNS and email.
However, for customer management, there are still many cases that rely on Excel or in-house formats. Then, there is a lot of risk that manpower will be needed unnecessarily, oversights will occur due to the huge amount of customer information, and thorough follow-up will not be possible. Above all, the security aspect is weak, and the risk of important customer information being leaked cannot be denied.
By introducing a customer management system, it is possible not only to provide comprehensive service and care to existing customers by status, but also to discover new customer targets based on purchase history and access history, etc., and take appropriate approaches. increase. The security level will also be significantly improved, which will greatly contribute to increasing the trust of stakeholders.
Read more: Ultimate guideline of appropriate system development flow
Difference Between the Core System and Business System
Let’s clarify the difference between a core system and a business system based on the information provided:
- Core System: A core system refers to a mission-critical IT system that supports the fundamental and essential business operations of a company. These systems are of utmost importance for the organization’s overall functioning and success. They directly manage core business processes, such as production management, sales management, and financial accounting. The primary focus of core systems is to ensure the stability and reliability of essential operations, and any malfunction can have an immediate and significant impact on the company’s management.
- Business System: On the other hand, a business system is a supporting system that aims to improve efficiency, save labor, and reduce costs for specific operations within the organization. Business systems are often targeted at individual departments or functions, such as customer relationship management, inventory management, and human resource management. While they play a crucial role in enhancing productivity and streamlining specific operations, their malfunction typically does not directly affect the core operations of the company.
In practice, there can be cases where a business system serves a role similar to a mission-critical system, depending on the specific product or operation being supported. This can blur the distinction between the two categories, and some systems may have characteristics of both core and business systems.
Regarding the development of systems, companies may choose to commission a system development company to build an original system tailored to their specific needs. This custom approach may require more time and cost compared to off-the-shelf products, but it allows for greater flexibility and the ability to combine and integrate multiple mission-critical systems and business systems. This pursuit of user-friendly uniqueness can bring significant benefits to the organization in terms of efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness.
In summary, while core systems are mission-critical and directly manage essential business processes, business systems provide support for specific operations to improve efficiency and reduce costs. The line between the two can sometimes be blurred, and custom-built systems offer greater opportunities to combine and integrate functionalities for unique advantages.
ERP is an Integration of the Core System and Business System
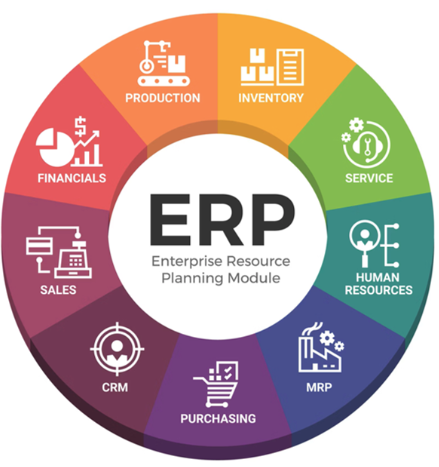
In addition to core systems and business systems, there is also a system called “ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning Module”. As we mentioned earlier, this refers to integrating multiple core systems and business systems that are outsourced to development companies and systematizing them so that they can be centrally managed (there are also ready-made products).
- ERP Integration and Centralized Management: ERP systems are designed to integrate multiple core systems and business systems, whether developed in-house or outsourced to development companies. The goal is to centralize the management of various departmental information and data. This includes functions such as inventory management, purchase management, sales management, production management, accounting management, personnel and payroll, and more.
- Real-time Data Linkage: One of the primary purposes of ERP is to link data in real-time, allowing for quick and accurate decision-making. This real-time data linkage enhances the ability to respond promptly to changing business conditions and provides a comprehensive view of the organization’s operations.
- Strengthening Business: The ultimate purpose of implementing an ERP system is to strengthen the organization. By effectively utilizing resources such as people, goods, money, information, and intellectual property, ERP enhances core business processes that form the foundation of the company.
- Essential for Corporate Value: The concept of ERP is essential for increasing corporate value. Through the streamlined integration and management of various systems and data, ERP enhances operational efficiency, reduces redundancy, and fosters better decision-making, ultimately contributing to the organization’s overall growth and success.
In summary, ERP systems play a vital role in centralizing and integrating various systems and data across the organization. By doing so, they facilitate real-time data linkage, enhance core business processes, and increase corporate value, making ERP an essential tool for modern businesses seeking improved efficiency and competitiveness.
Main Core Systems and Business Systems Integrated with ERP
ERP systems are sold as products in various forms, such as cloud, on-premise, and packaged. In addition, when pursuing originality, it is often the case that development is outsourced to a developer.
In any case, ERP includes the following systems:
- Production control
- Sales management
- Development management
- purchase management
- Purchasing management
- Labor management
- HR management
- Adoption management
- Payroll accounting management
- Financial Management
- Customer management
- Asset management
- Receivables management
- Debt management
- Inventory control
- Warehouse management
And so on.
There are also systems that are not included in the product, so when introducing it, it is necessary to carefully examine the necessary functions and select the most suitable one for your company.
How to Choose the Core System and Business System/ERP
Finally, let’s explain the key points when choosing a core system, business system, and ERP, and how to choose a contractor when outsourcing these.
Choosing the right core system, business system, or ERP, and selecting the right contractor when outsourcing these projects are critical decisions for a company’s success. Here are key points to consider when making these choices:
Points to Consider When Choosing a Service
There are six points to consider when choosing a service.
- Clarify the purpose of the introduction within the company
- Check if it has the features you need
- Make sure it’s extensible and customizable
- Conduct a simulation to see if the company’s personnel can master it
- Check your support system
- Don’t choose based on budget alone
Let’s dig into each one.
Clarify the Purpose of the Introduction Within the Company
Whether it is a core system, a business system, or BRP, if the purpose of the introduction is vague, the probability of failure will increase greatly no matter what service is used. In any business, it is the employees of the company that lead it to success, and the top management, executives, and leaders who oversee it, not the system itself.
It is important to keep in mind that just introducing a new system will not magically solve various problems and make operations more efficient.
When outsourcing to a system development company, there is always a process called “requirement definition” first. Here, we will thoroughly discuss “what”, “for what purpose”, “what kind of usability and operability”, “by when” and “how much” to develop. If the purpose of the introduction on the ordering side is ambiguous, the development company will be confused about what to proceed and how to proceed.
Therefore, let’s make the purpose as concrete as possible, for example, “I want to link production management and sales management, use the customer management function in real-time, and send thank yous, recommendations, campaign promotional emails, and e-mail magazines.” If you do this well in advance, the chances of reaching a service without mistakes will increase.
Check if It has the Features You Need
After clarifying the necessary functions and systems within the company, the next step is to find a service that meets those needs. If there is something that seems to be applicable, let’s investigate in detail by requesting materials or making inquiries.
Costs can vary greatly depending on which service provider you use. Therefore, it will be necessary to carefully examine whether the effect commensurate with the cost can be obtained.
Make Sure it’s Extensible and Customizable
Whether it is a core system or a business system, scalability is often required according to business flow and strategy rather than using it alone. It should also be customizable to fit your own style. Don’t forget to choose not only for the immediate purpose but also for how far the flexibility in that area will work, looking ahead to the future.
Conduct a Simulation to See if the Company’s Personnel Can Master It
The introduction of new systems is often decided by upper management, which has decision-making power. Then, the employees who actually use the system have no room to interject their own opinions and have no choice but to use what they are given. However, if those people find it difficult to use, there is no point in introducing a new system.
Therefore, instead of forcing the ideal system on the upper management, listen carefully to the opinions of the people in charge of the field who use it every day, and then select the service that best suits your company comprehensively. Take care.
Check your Support System
No service is perfect the first time. It is almost certain that there will be situations where a problem occurs, or you do not know how to deal with it, or how to operate it. Support and maintenance are what you can count on.
In the case of mission-critical systems in particular, if recovery takes a long time, there is a great possibility that the customer will be greatly damaged, and the company’s credibility will be greatly damaged. Therefore, be sure to check in advance what conditions you can receive support and maintenance after the introduction, including costs.
Don’t Choose Based on Budget Alone
When introducing a new system, there is a strong tendency to focus too much on the budget. To some extent, it may be unavoidable. However, it still costs money, so in the long run, it will be a loss if it is cheap or not. If you can introduce an optimal system that hits the mark in the true sense, you may gain many times in the future, so let’s value the idea of emphasizing functionality.
How to Choose a Subcontractor
Next, we will explain the important points to consider when outsourcing your system development to a third-party development company. There are five key factors to keep in mind:
- Check the subcontractor’s achievements
- Ensure Relevant Experience
- Assess Their Financial Standing
- Request Multiple Quotes
- Stay Involved in the Development Process
Check the Subcontractor’s Achievements
When choosing a developer, it’s crucial to thoroughly assess their past track record. Some companies may falsely claim extensive experience and capabilities, even without a proven record. To ensure reliability, consider seeking recommendations from trusted business partners or acquaintances. Working with someone recommended by a trusted source increases the likelihood of a meticulous job.
Additionally, don’t assume that the developer must be a domestic company. Exploring offshore development, such as outsourcing to Southeast Asia, like Vietnam, can be beneficial. Many skilled professionals there possess comparable expertise to Japanese engineers, and development costs can be significantly lower. Moreover, the “laboratory type” development model is a great option. It involves creating a dedicated team for your company, allowing you to request various tasks during the contract period, just as you would with in-house engineers. This model offers high mobility and responsiveness, ensuring a successful collaboration.
Ensure Relevant Experience
When evaluating development achievements, it is essential to verify if the development company has experience in creating systems within the same genre as the one you are planning to develop. Keep in mind that core systems may be more complex than business systems, and ERP systems can be even more intricate. If possible, consider having the development company build a prototype or a small-scale version of the system. This way, you can see firsthand how well it aligns with your company’s image and meets your specific needs. This hands-on approach will help you make an informed decision about choosing the right development partner for your project.
Assess Their Financial Standing
When embarking on a system development project from scratch, it’s crucial to be aware that the development period can span several months to a year. While a company with a robust management structure can navigate this process smoothly, there are instances where management faces challenges, leading the company to abandon the project. This situation can be concerning, especially if you’ve already paid a portion of the development cost, and there’s a risk of not getting a refund.
Apart from the financial aspect, a significant delay in system introduction can result in substantial losses for the management. It’s essential to exercise caution and carefully consider the financial stability and credibility of the development company before initiating the project. Ensuring that the chosen contractor is reliable and has a solid track record can help mitigate risks and reduce the likelihood of facing such challenges during the development process.
Managing a system development project effectively requires vigilant oversight and frequent communication with the development team. Being proactive in addressing any potential issues and staying engaged throughout the process can help avoid significant delays and unexpected setbacks. By being cautious and well-prepared, you can maximize the chances of a successful system development project that meets your expectations and delivers the desired results.
Get Multiple Quotes
Don’t limit yourself to one company from the beginning, ask for quotes from multiple companies at the same time. Even with the same development project, the method of proceeding with the project, the way of thinking, and, of course, the amount of money vary depending on the company. You can learn by comparing them, and you can also refer to one company’s quote and haggle with another company. And finally, make sure to choose the company with the best cost performance.
Stay Involved in the Development Process
This is a little different from the point of selecting a contractor, but when developing a system, it is extremely dangerous to leave everything to the contractor. Because the other party is a professional, if they see that we are amateurs in development, they will proceed with things from the standpoint of having more experience and knowledge than us, and they will push the way they think is right. There are some things that cannot be undone after the product is completed. Even if you can, you may have to pay additional costs. Therefore, do not forget to check the progress management and development status frequently.
Summary
The characteristics and differences of core systems, business systems, and ERP have been thoroughly explained. With the increasing necessity of Digital Transformation (DX) across industries, there is a strong demand to review and update IT systems, regardless of a company’s size.
Legacy systems that are too old risk becoming obsolete, and the ongoing shortage of human resources makes it essential to develop efficient and labor-saving systems. As a business owner or decision-maker, it is crucial to seriously consider updating your systems to stay competitive and meet the demands of the evolving business landscape.
Relipa, with over 7 years of experience in developing web application systems, has established itself in the market. Our team of experts is proficient in web programming languages and stays flexible by applying the latest frameworks. We are dedicated to meeting all customer requirements, from design to implementation, ensuring high-quality results and fast project completion times.
Moreover, we actively consult with our clients to refine their ideas and assist them in making the best decisions for their projects. Our commitment and professionalism are aimed at delivering customer satisfaction. If you are seeking a reliable partner to embark on your system development journey, we believe Relipa can be your ideal choice.
If you are looking for a reliable and professional system development partner, please contact us.