What Is n8n Node? Types Of Functions And Basic Operations
In recent years, automation has become an integral part of both daily life and business operations, helping organizations streamline processes and improve efficiency. To visualize this, consider a factory production line. Each stage, such as material input, molding, firing, inspection, and packaging, performs a specific function, yet all stages are tightly coordinated to deliver a finished product with consistent quality.
The software world follows a similar principle. N8n is an open-source workflow automation platform that enables users to build such automated “production lines” for digital processes. n8n organizes each process as a node, visually connected to define how data moves and is handled. When these nodes work together, they form a complete automation flow, much like a digital production line.
This blog will explain what an n8n Node is, why it matters, and introduce the main node groups, basic operations, and key considerations when using them.
What is n8n Node?
A node is the fundamental building block in n8n, responsible for handling data, interacting with external services, or retrieving information from them.
Certain nodes, such as trigger nodes, act as the starting point of a workflow by waiting for a specific event or condition to occur. Other nodes take incoming data, apply processing logic, such as transformation or conditional routing, and then pass the results to subsequent nodes.
Through thí node-based structure, n8n offers a visual programming experience similar to flowcharts or circuit diagrams. Users can design and understand automation flows intuitively, without the need for manual coding. This approach not only simplifies maintenance and updates but also makes n8n accessible to non-engineers while remaining powerful enough for advanced use cases.
Why Nodes Matter in n8n
Nodes are the core mechanism that turns automation ideas into working workflows. They define how each step is structured and how data moves across the entire process.
Seamless Integration with Apps and Services
- Node makes it easy to connect various applications and services without writing complex code.
- Instead of interacting directly with individual APIs, Node provides pre-packaged functionality.
Flexible Data Handling
- With nodes, you can flexibly extract, convert, filter, and combine data.
- Combine multiple data sources for smarter, more efficient automation.
Complex Automation without Coding
- N8n’s Node-based architecture allows you to create sophisticated automation flows with drag-and-drop operations, without any specialized programming knowledge.
- No deep programming expertise is required, and workflows remain easy to understand and maintain.
Modular and Scalable Workflow Design
- Easily adjust your automation process by simply adding, removing, or rearranging nodes.
- It is highly scalable, allowing you to flexibly respond to changing business needs.
Key Components of an n8n Node
Node Label
This is the identifier assigned to a node within a workflow. Renaming the label helps clarify the node’s function at a glance, making complex workflows easier to read and manage.
Node Type
Indicates the category to which the node belongs and the services it is linked to. For example, Google Sheets, HTTP Request, etc.
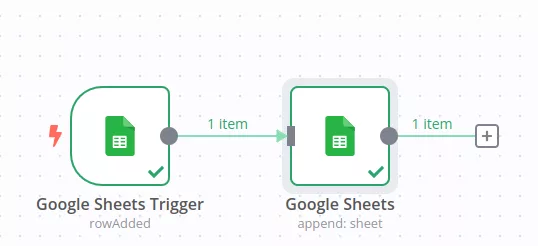
Parameters/Settings Area
This section controls how the node behaves in practice. It is where you define the specific action to execute, configure credentials, and set required input values that determine the node’s operation.
Input/Output Anchors
Most nodes include input and output points that determine how data is passed between steps. By connecting these anchors, you define both the execution sequence and the data flow, enabling the overall workflow logic to be constructed visually.
Credentials
When a node connects to an external service, authentication details are often required. n8n provides a secure credential management system, allowing credentials to be stored safely and reused across multiple nodes and workflows.
Main Node Groups and Their Core Functions
Role-based Classification
One of the most common ways to categorize nodes is based on the role they play within a workflow.
Trigger Nodes
Trigger nodes define how and when a workflow starts. Every workflow requires at least one trigger node, without it, the automation cannot run automatically.
The primary function of atrigger node is to listen for specific events or conditions. Once an event is detected, the trigger node initiates the workflow, passes the initial data to the next node, and begins execution.
n8n provides various types of trigger nodes to support different use cases, including:
- Schedule (formerly Cron) Node: Runs a workflow according to a defined schedule, such as hourly, daily, or at specific intervals.
- Webhook Node: Launches a workflow when an external service sends an HTTP request.
In addition to generic triggers, n8n also offers a wide range of app-specific trigger nodes. For example:
- Gmail Trigger: Starts a workflow when a new email is received.
- Google Forms Trigger: Detects new form submissions and initiates the workflow.
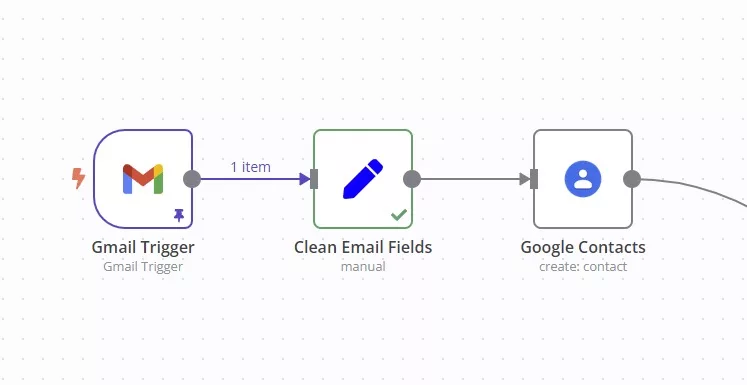
In essence, trigger nodes function as the “starting mechanism” of a workflow, enabling external events or predefined conditions to activate automation flows seamlessly.
Action Nodes
Once a workflow is initiated by a trigger node, action nodes handle the actual processing steps. They represent the most diverse group of nodes in n8n, supporting a wide range of automation use cases.
Action nodes execute specific operations based on the data passed from the previous node. These operations may include sending notifications, storing or updating data, modifying system records, or interacting with external applications and services.
Common examples of action nodes include:
- Send Email Node: Sends notification or alert emails.
- Google Sheet Node: Performs actions such as appending new rows or updating existing data.
- HTTP Request Node: Enables communication with any API.
Beyond executing actions, these nodes can also filter, sort, and transform data. This allows you to refine and structure information before passing it to subsequent nodes, providing greater flexibility and control over the overall workflow.
Classification Based on External Service Integration
Another common way to categorỉze nodes is by whether they operate independently or interact with external services and applications.
Core Nodes
Core nodes are built-in components of n8n that form the backbone of workflow logic and data processing. They do not rely on external services and are primarily used to control flow, manipulate data, and handle conditions within a workflow.
These nodes are essential for creating flexible and intelligent automation logic.
Typical core nodes include:
- IF Node: Splits the workflow based on true/false conditions.
- Switch Node: Routes data into multiple branches according to defined values.
- Set Node: Creates new data fields or updates existing ones.
- Function/Function Item Node: Uses JavaScript to perform advanced data processing.
- Merge Node: Combines multiple data streams into one.
- Edit Fields Node: Selects, renames, or modifies data fields.
- No Operation (NOP) Node: Serves as a placeholder for debugging or flow control.
By combining core nodes, you can implement complex logic such as conditional branching, data transformation, and basic error handling without leaving the workflow editor.
Integration Nodes
Integration nodes enable n8n to connect seamlessly with external applications, cloud services, databases, and APIs. This group powers n8n’s ability to automate real-world business processes across hundreds of platforms.
Popular integrations include:
- Google Workspace: Gmail, Google Sheets, Google Drive
- Social Platforms: Facebook, X
- Collaboration Tools: Slack, Telegram, Microsoft Teams
- CRM Systems: HubSpot, Salesforce
- Databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB
Each integration node provides actions and triggers tailored to its service. For example:
- Google Sheets Node: Supports operations such as Get Rows, Append Row, and Update Row.
- Slack Node: Allows workflows to send messages using the Send Message action.
The integration node library is continuously expanding, enabling broader connectivity and smoother automation across systems.
Community and Custom Nodes
Beyond standard and core nodes, n8n supports extensive customization through Community Nodes and Custom Nodes, making the platform highly extensible.
- Community Nodes: Developed and shared by the n8n community. They often support niche tools, emerging services, or industry-specific use cases that are not officially integrated. These nodes can be installed easily and added to workflows with minimal setup.
- Custom Nodes: For highly specific requirements or internal systems, n8n allows you to build custom nodes. While development requires JavaScript or TypeScript knowledge, custom nodes provide full control over functionality. This is particularly valuable for integrating proprietary APIs or automating internal business logic.
Together, community and custom nodes highlight n8n’s open and extensible architecture, allowing teams to adapt the platform to virtually any automation scenario.
How Does n8n Node Work?
Node Input and Output: The Foundation of Data Flow
With the exception of trigger nodes, most n8n nodes operate by receiving input data and producing output data. This input-output mechanism forms the core of data flow within a workflow.
Input Data
In most cases, a node receives the output generated by the preceding node. This input is structured as a collection of items, where each item is represented as a JSON object.
Output Data
After processing the incoming items, the node generates a new set of items as output. These outputs are then passed sequentially to the next node, enabling the workflow to execute step by step.
Testing and Debugging
The n8n interface allows you to inspect both input and output data at each node execution. This makes it easier to understand data structures, trace logic, and debug workflows during development.
JSON Data Handling in n8n
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is the primary data format used throughout n8n. Data exchanged between nodes, and most interactions with external APIs are handled in JSON format.
JSON Structure
JSON consists of key-value pairs and is designed to be both human-readable and machine-friendly. In n8n, each input and output item of a node is treated as a JSON object.
Accessing JSON Values
Workflows often reference specific fields, such as email or name, from node outputs. This enables flexible data extraction, transformation, and conditional routing within workflows.
A solid understanding of JSON makes it easier to work with APIs and design accurate, efficient data processing between nodes.
Basic Node Operations: Adding, Connecting, and Configuring
Working with nodes in n8n is designed to be straightforward and intuitive. The user interface enables you to build workflows visually using simple drag-and-drop interactions.
Adding a Node
Click the “+” icon on the workflow canvas to open the node selection panel. From there, you can search for nodes by name, function, or category, such as core nodes or integration nodes. Selecting a node will place it directly onto the canvas.
Connecting Nodes
To define the data flow, drag a line from the output anchor on the right side of a node to the input anchor on the left side of the next node. This connection determines both the execution order and how data is passed between nodes.
Configuring Node Settings
Selecting a node opens the parameters panel on the right-hand side of the screen. In this panel, you can choose the action to perform, configure credentials, set input values, and preview data as it flows through the node.
Thanks to this intuitive interface, even first-time users can quickly assemble and manage complex automation workflows by seamlessly adding, connecting, and configuring nodes.
Points to Consider When Using n8n Nodes
Always Output Data
When enabled, the node will return an empty item even if no data is produced during execution. This allows the workflow to continue despite missing data. However, caution is required, especially when used with conditional nodes such as IF nodes. Since an empty item is always passed forward, this setting can unintentionally trigger repeated executions or infinite loops if not handled carefully.
Execute Once
This option forces the node to run only once using the first incoming data item, ignoring any additional items. It is particularly useful for actions that should occur a single time, such as API calls or sending notifications. For example, even if ten data items are received, the node will execute only for the first one.
Retry on Failure
When enabled, the node automatically retries execution until it succeeds. This is especially helpful for handling transient issues such as network interruptions or temporary API failures. By retrying automatically, this setting improves overall workflow reliability when working with external services.
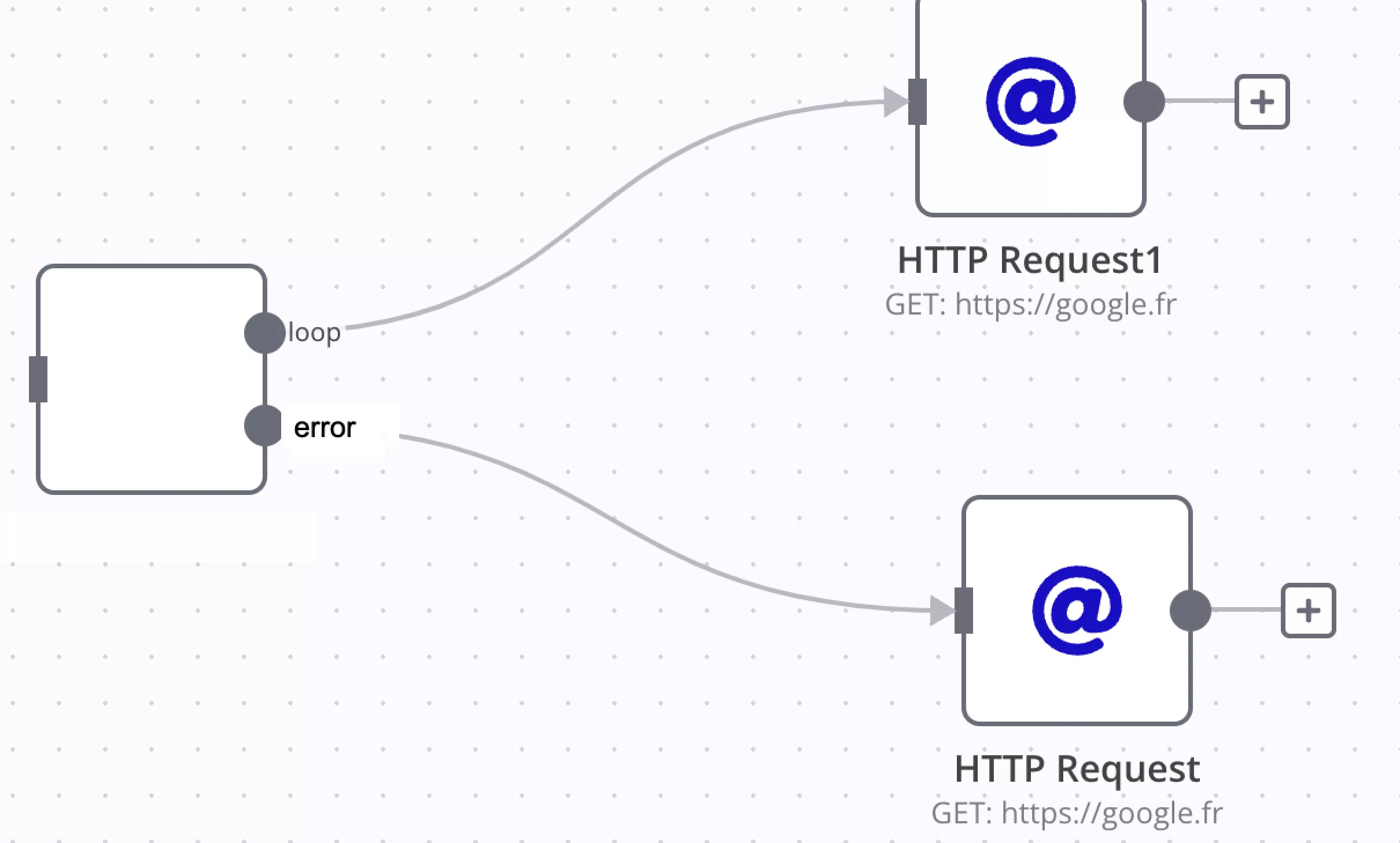
Error Handling Behavior
You can define how the workflow should behave when a node encounters an error:
- Stop Workflow: The entire workflow halts immediately when an error occurs. This option is appropriate for critical processes where incorrect data handling or duplicate execution must be avoided.
- Continue: The workflow proceeds to the next node using the last valid data, even if an error occurs. This is useful when minor errors can be safely ignored without disrupting the rest of the process.
- Continue with Error Output: Error details are passed to subsequent nodes while the workflow continues. This enables flexible error-handling strategies, such as sending error notifications to Slack or storing error logs in a database.
Using Node Notes
Node Notes allow you to document the purpose, conditions, or special configurations of individual nodes. When the “Show notes in flow” option is enabled, these notes appear directly on the workflow canvas as subtitles. This makes complex workflows easier to understand and maintain, especially during reviews or handovers.
Conclusion
Just as a manufacturing line delivers high-quality products when each stage performs its role precisely, an n8n workflow achieves maximum automation efficiency when every node functions as intended. Each node contributes to the overall flow, and their coordination determines the stability and effectiveness of the automation.
With over nine years of experience in software development, including AI, blockchain, and digital transformation, Relipa is trusted by leading enterprises globally. Beyond strong technical expertise, we focus on understanding real business challenges to deliver practical, tailored solutions.
Contact Relipa today to explore expert consulting and optimized workflow automation solutions designed for your business needs.