What Is Google Bard? Introducing How To Start, How To Use, And Differences From ChatGPT
When Google launched its AI chatbot Google Bard, it didn’t have much of an edge over the likes of Bing Chat and ChatGPT. In fact, the initial launch was a bit of a disaster, with Bard’s incorrect answer in a Google ad prompting the company’s stock price to drop 8% at one point.
On May 11, 2023, at the I/O developer conference, Google introduced Google Bard again, hoping to gain more popularity. Similar to Bing Chat secretly using OpenAI’s GPT-4, Bard has been using PaLM 2 for a period of time. Seeing people engaging with Bard in creative and imaginative ways is amazing.
This would be a good opportunity for Bard to use his brain. Google is eliminating the waitlist, making Bard available to everyone in over 180 English-speaking countries, and starting to support Japanese and Korean. Google pledged to support 40 languages in the near future. In addition, Google has announced a number of new features for Bard, such as multimodal queries that can work with images, so you can use images as prompts or ask Bard to explain.
But this momentum is just the beginning. In this article, we will explain the following points to assist users in taking advantage of Google Bard
- What is Google Bard?
- Introducing a new way to collaborate with Google Bard
- Compare Google Bard and ChatGPT
- Alternative to Google Bard
What is Google Bard?
Google Bard: The Definition
Google Bard, like ChatGPT, is a conversational AI chatbot that can generate any kind of text. Bard will answer any question as long as it doesn’t violate Google’s content policy. Google is apt to reform Google Bard to replace its existing voice assistant named Google Assistant.
Google Bard was built based on Google’s own Large Language Model (LLM), termed LaMDA (Language Model for Dialogue Applications). Being equivalent to OpenAI’s GPT-3.5, which is the backbone of ChatGPT, Google AI engineers have been training LaMDA with a myriad of parameters to force AI to “learn” natural language. It turned out that a generative AI chatbot can answer most users’ questions/prompts in surprisingly natural, conversational language.
LaMDA was originally announced at Google I/O in 2021, but remained a prototype and was never released to the public. However, when ChatGPT appeared at the end of 2022, Google started developing chatbots equipped with LaMDA to compete. Google Bard was first announced in February 2023.
How to Use Google Bard
To use Google Bard, go to bard.google.com. As with all Google products, you will need to log in with your Google account. You’ll also need to agree to Google’s Terms of Service, but you can start using Google Bard right away. Like ChatGPT, Bard is mostly an empty text field that says “type your message here”. Type a prompt or question, and Bard will suggest the answer.
Fortunately, Google gives us some random ideas that are different every time we open Bard. The first given example is
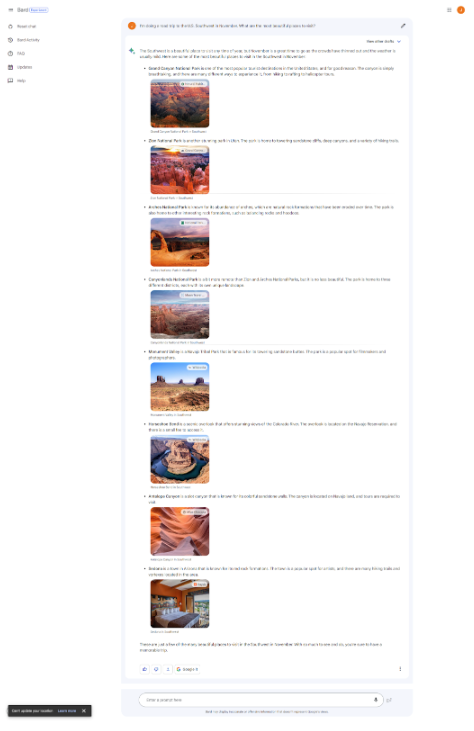
- “I’m doing the road trip to the US Southwest in November. What are the most beautiful places to visit?”
- How would I use Python to generate the “scholar’s mate” in chess?
- “What’s a fast, balanced vegetarian meal for me to make? It should be high in protein and fiber.”
Clicking on Bard responded as follows. Especially, Google Bard can generate answers with images, which makes them more appealing than GPT.
Features of Google Bard
- Google Integration: Bard’s technology is designed to integrate seamlessly with Google’s ecosystem, giving users access to a wealth of information from various Google products such as Google Search and Google Scholar. These resources allow Bard to provide users with real-time, up-to-date information. Additionally, this integration leverages your search history and preferences to better understand your needs and interests, enabling a personalized experience.
- Citing Sources: Google tries to make citations more accurate. If Bard brings in a block of code or quotes other content, just click the annotation, and Bard will underline that part of the response and link to the source.
- Sentiment Analysis: Bard has a remarkable feature that allows you to assess the sentiment expressed in text. This feature allows you to measure public opinion, understand brand reputation, and create a tailored emotional response to your customers.
- Real-time Language Translation: Google Bard is equipped with advanced NLP features that allow instant language translation. This makes it an essential tool for individuals who communicate in multiple languages, as it removes language barriers and facilitates better global collaboration.
- Voice interaction: Google Bard offers more than just text-based communication. It also features voice-based interaction, making it an efficient virtual assistant for a variety of tasks. Users can use their voice to give commands, access information, search the web, set appointments, and much more. This feature is especially useful for busy people and those with accessibility needs, as it allows hands-free interaction with Google Bard.
- Coding: Bard can help with programming and software development tasks such as code generation, debugging, and code explanation. Google is launching these features in over 20 programming languages, including C++, Go, Java, JavaScript, Python, and Typescript. You can also easily export your Python code to Google Colab. No copy-paste is required. Bard also supports writing functions for Google Sheets. Besides generating code, Bard can also help explain code snippets. This is especially useful when learning to program for the first time or when you need additional help understanding what a block of code outputs.
- Makes interaction with Bard more visual:
- Google Bard users can now directly ask Bard to display images in search results. If you ask “What are the must-see sightseeing spots in Kyoto?”, you will get a kind answer with plenty of visuals in addition to the text, so you can better understand what you are looking for.
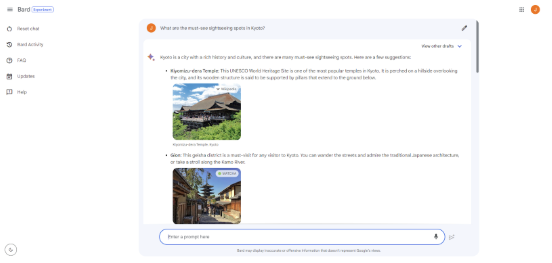
Image credit: Google
- In addition, you can now include images in your prompts as well as text, allowing your imagination and creativity to flourish. To achieve this, Google brought the power of Google Lens to the Bar. For example, let’s say you want to use a photo of your dog to have a good time. Upload that photo and ask Bard to write a funny caption about these two. Bard uses Google Lens to analyze photos, detect dog breeds, and create some creative captions – all within seconds.
From now on, you’ll be able to use Google Bard with Google Applications, such as Docs, Drive, Gmail, etc. Google will introduce new ways to spark your imagination and curiosity by integrating features and services into your Bard experience. Of course, you can always control how you use these tools and extensions in your privacy settings.
Bard can also use extensions from external partners to consume any service on the web, allowing you to do things that weren’t possible before. In a few months, Adobe’s family of creative generative AI models, Adobe Firefly, will be integrated into Bard to easily and quickly transform your creative ideas into high-quality images. Adobe Express can be further edited and added to the design.
For example, let’s say you’re planning a birthday party for your unicorn-loving 7-year-old and want a fun image to send with the invitation. Create an image of a unicorn and a cake”, and Bard can generate it in seconds while adhering to Adobe’s high standards of quality and ethical responsibility.
Google wants Bard to be the source of inspiration for your creativity, productivity, and curiosity. That’s why Google is working on handy apps from Bard and Google, as well as connections with partners like Kayak, OpenTable, ZipRecruiter, Instacart, Wolfram, Khan Academy, etc.
By working with Google’s tools and other great services on the web, you’ll be able to collaborate fluidly with the most capable large-scale language models. Combining human imagination with Bard’s generative AI capabilities, the possibilities are endless. You are free to use it to support any creativity.
How Does Google Bard Work?

Google Bard is powered by PaLM 2, Google’s own state-of-the-art large-scale language model (LLM), announced at Google I/O 2023.
PaLM 2, a further evolution of PaLM announced in April 2022, enables Bard to perform more efficiently, perform at a higher level, and solve the problems of its previous version.
Early versions of Bard used a lightweight model version of LaMDA because it requires less computing power and can be scaled up to a large number of users.
LaMDA is based on the Transformer, which is a neural network architecture invented by Google in 2017. Strikingly, the language model that ChatGPT works on, GPT-3, is also built on Transformer, according to Google.
Some of the most popular AI chatbots today, such as ChatGPT and Bing Chat, use the GPT series of LLMs, so using their own LLMs, LaMDA and PaLM 2, is a bold move by Google. It’s a radical decision.
Bard is equipped with a “lightweight version” of LaMDA.
LaMDA is a large-scale language model, trained on a dataset of public conversations and web data.
There are two key factors related to the training described in the related research paper (downloadable as a PDF here). LaMDA: Language Models for Dialog Applications。
- Safety: Tuning with data annotated by crowd workers ensures the safety of the model.
- Grounded: LaMDA can be factually grounded by external knowledge sources (information retrieval, which is search).
The LaMDA research paper states:
“…a factual basis allows us to refer to external knowledge sources such as information retrieval systems, language translators, calculators, etc.”
Google quantifies factuality using the metric of evidence and found that Google’s approach allows the model to generate responses based on known sources, rather than just responses that sound plausible.
Google used three metrics to evaluate LaMDA’s output.
- Sensibleness: A measure of whether an answer makes sense.
- Specificity: Measures whether an answer is general, vague, or contextual.
- Interestingness: A measure of whether LaMDA responses are insightful or arouse curiosity.
All three metrics were judged by crowdsourced evaluators, and the data was fed back to the machine for continuous improvement.
The LaMDA research paper concludes that crowdsourced reviews and the ability of systems to do fact-checking on search engines were useful techniques.
A Google researcher wrote:
“We have found cloud annotation data to be an effective tool with significant benefits. We also called external APIs (such as information retrieval systems) to allow generated responses to be distributed to known sources. On the other hand, we have found a way to significantly improve groundedness, which is the definition of how many claims that can be referred to and confirmed are included.”
Why did Google Decide to Announce Google Bard Now?
ChatGPT has heated up the race of Artificial Intelligence since its release. Less than a week after its launch, ChatGPT has over 1 million users. ChatGPT is the fastest-growing app of all time, according to an analysis by the Swiss bank UBS. Because of this success, other tech companies, including Google, are eager to enter the race to secure their own market leader position.
In the same week that Google announced Bard, Microsoft announced a new Bing with improved algorithms. This Bing is powered by the next-generation OpenAI large-scale language model, customized specifically for search.
Read more: Unlocking the Power of ChatGPT API (gpt-4): A Complete Guide
Compare Google Bard and ChatGPT
What Bard and ChatGPT Have in Common
- Natural Language Processing: Bard and ChatGPT utilize advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms to generate human-like text based on user input.
- User Interface: Each platform offers a user-friendly interface that allows users to quickly ask questions, enter prompts, and generate sentences with minimal effort.
- Versatility: It is possible to generate different types of content, such as social media updates, product descriptions, and creative pieces of art like songs and poems.
- Frequent Updates: The developers of both platforms continuously update their respective AI models to improve performance and provide better results to users over time.
Differences Between Bard and ChatGPT
|
ChatGPT |
Bard |
|
| Development Company | OpenAI | |
| Language model | OpenAI’s Generative Pre-training Transformer 3 (GPT-3) specially tuned version of Generative Pre-training Transformer 4 (GPT-4) | Google’s Language Model for Conversational Applications (LaMDA) |
| Data source | ChatGPT was trained on a large text dataset containing content collected from Common Crawl, Wikipedia, books, articles, documents, and the open internet. But that source ends in 2021, limiting the latest world events and research. | Bard was trained on the infinitive dataset, which contains Common Crawl, Wikipedia, documents, web conversations, and interactions. Bard will likely search the web in real-time to find the latest answers to questions and research. |
| Pricing | ChatGPT is free for all users. ChatGPT Plus costs $20/month and includes accessibility in peak times, faster response times, and priority access to new features such as GPT-4. | Bard is free for users with access |
“In this article, we examine and compare the answers given by ChatGPT and Google BARD on three different tasks to find out which AI tool performs better in terms of accuracy, aptitude, information synthesis, and coding.
Accuracy and Suitability of ChatGPT and Google Bard
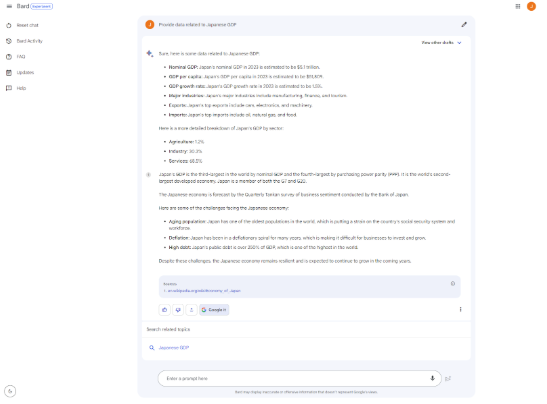
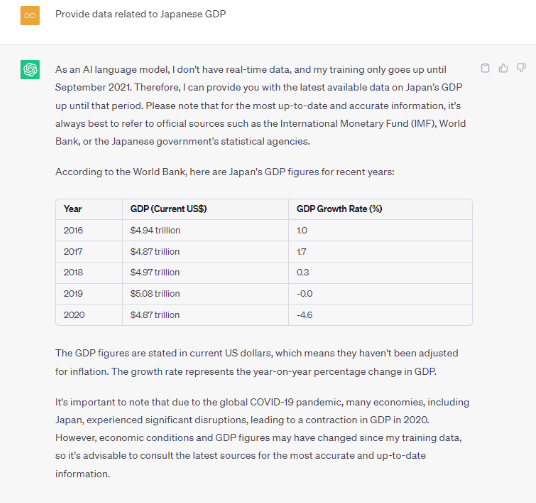
Question: Provide data related to Japanese GDP (2019-2023)
Upon close analysis of the responses provided by both ChatGPT 4 and Google Bard, ChatGPT provides an easy-to-read table of nominal GDP and growth rates. On the other hand, Google Bard can cite a source for the data that it provides. Bard can also provide predictions for 2023. By contrast, GPT-4 can only provide data for 2019 and 2021.
🏆 Winner: None
The Ability to Summarize Information Between ChatGPT and Google Bard
Question: Describe what is API to people who don’t have experience in coding.
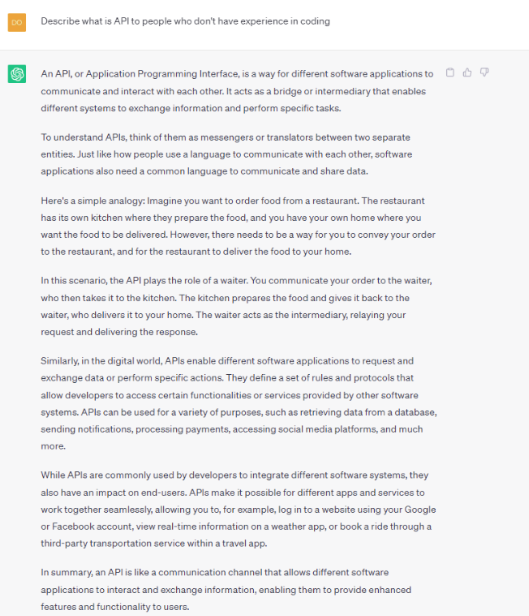
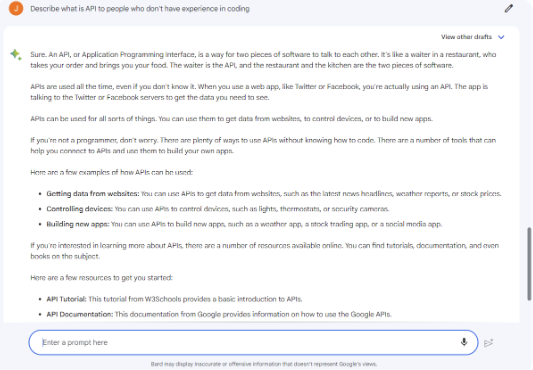
When I asked each AI tool to explain its API to a non-programmer, both gave solid answers.
While ChatGPT 4 employed the restaurant waiter analogy to illustrate the role of APIs in software communication, Google Bard illustrates the concept through the example of a weather application that utilizes the OpenWeatherMap API to retrieve weather data. explained.
Both explanations are clear and concise, but ChatGPT’s answer provides a more detailed explanation of how APIs are utilized in software development. Apart from a comprehensive explanation, ChatGPT also provides easy-to-understand metaphors, such as “To understand APIs, think of them as messengers or translators between two separate entities. Just like how people use a language to communicate with each other, software applications also need a common language to communicate and share data”. By virtue of a digestible piece of information, non-technical readers can grasp a firm grounding of knowledge about API.
🏆Winner: ChatGPT
The Ability to Code of ChatGPT and Google Bard
Question: Write a piece of code to build a chess game app
The coding proficiency of ChatGPT and Google Bard enables them to generate HTML and CSS code to create a chess game application. ChatGPT 4’s response offers a comprehensive solution, providing well-designed layouts for chess game apps. The resulting HTML and CSS code accurately depicts a chessboard with pieces positioned correctly at the start. Notably, the code incorporates CSS classes for each chess piece, utilizing images to represent them. This response serves as a robust starting point for the development of chess game applications, demonstrating the potential of these advanced language models in coding tasks.
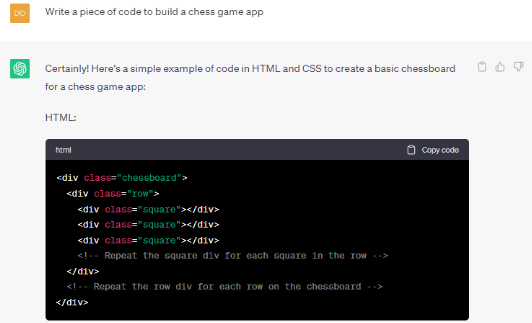
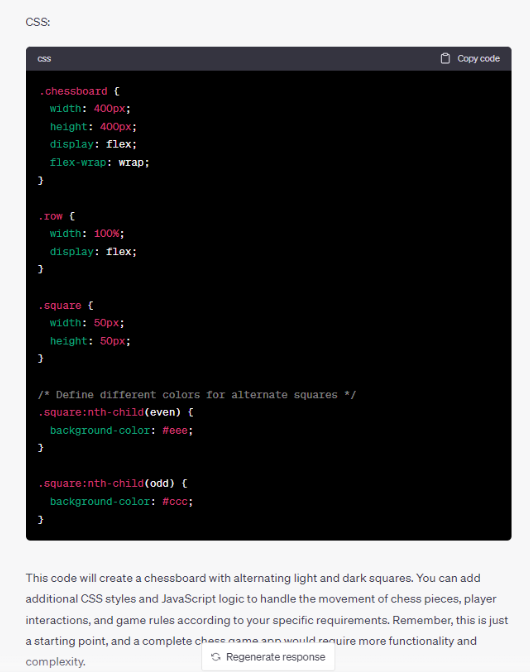
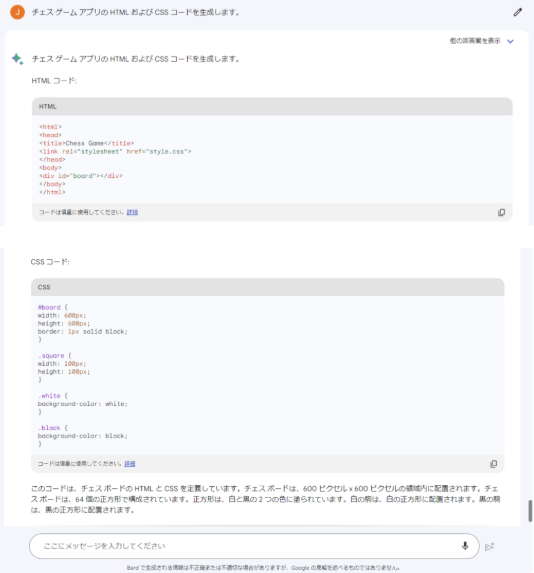
In contrast, the Google Bard reply simply presents the HTML and CSS of a basic 8×8 chessboard with no pieces. The chessboard layout is well established but falls short of providing the key details needed to create a fully functional chess game app.
🏆Winner: ChatGPT
Bard Provides a Better UX (User Experience)
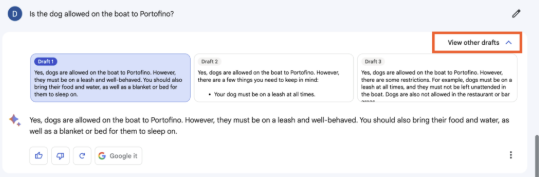
Bard is light-years ahead in terms of user-friendly interface. Much easier to read than ChatGPT’s chunky text. Formatted text not only looks better, but you can also edit your question after you ask it, and view multiple prepared answers in “View other drafts”.
Also, all responses have a CTA of “Google it” so you can see the source.
🏆Winner: Bard
Bard Will Be a Streamlined Version of Google Search, but ChatGPT Belongs to Bing
Bard’s ability to integrate information, no matter how complex the topic, into an easy-to-understand format which means it could ultimately improve the way people find information.
Google has already hinted that Bard will be integrated into Google Search. In other words, AI simplifies complex topics and returns information in an easy-to-understand format, giving you insight into different perspectives. (This is especially true for topics that don’t have a single correct answer).
Image credit: Google
Meanwhile, Microsoft already has some of OpenAI’s tuned GPT-4 models
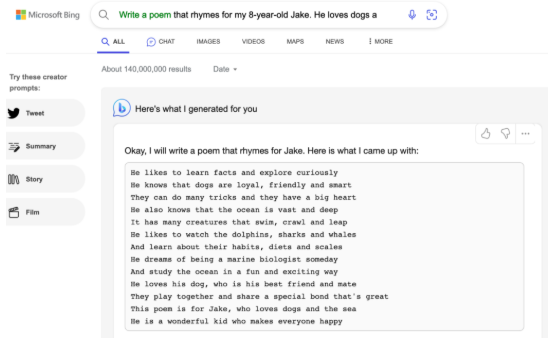
Bing, gives users a ChatGPT-like experience in the search bar. However, it’s still pretty limited and users have to join a waiting list to get the full experience.
🏆 Winner: None
So what do future Bard users need to know?
- Bard has a more up-to-date knowledge base because it’s taken from data on the internet. This is very different from ChatGPT, which was trained on data up to 2021.
- Bard will be integrated into Google’s search engine to simplify how people access information across complex topics.
- Bard is designed to improve research and understanding across education, business, and other fields, while ChatGPT focuses on text functionality.
- Bard is expected to provide more precise information, but ChatGPT needs careful prompting to generate more detailed responses.
Bard vs ChatGPT: Which is Better?
When choosing between ChatGPT and Google Bard, it’s crucial to consider that both AI models are designed to handle specific aspects with careful attention to detail. ChatGPT excels in generating and condensing text, while Google Bard excels in providing pertinent information related to your query. However, it’s important to note that both tools are still in their early stages of development, and only time will reveal which one outperforms the other.
Read more: Maximizing ChatGPT: A Guide to Using and Exploring ChatGPT’s Use Cases
Alternatives to Google Bard
ChatGPT wasn’t born from scratch. AI chatbots have been around for some time, albeit in a less versatile form. Several startups were working on similar chatbot technology, but were never able to catch on to GPT. Competitors Bard will face at launch include:
Microsoft’s Bing
The partnership between Microsoft and OpenAI intends to offer exactly what Google offers with Bard: an AI-powered search that recognizes natural language queries and gives natural language responses. When a user executes a search query, they are presented with standard Bing search results and GPT-4-generated answers, and can even interact with the AI about the answers.
Chat sonic
ChatSonic is an AI chatbot that uses Google search and is marketed as a “superpowered ChatGPT alternative”. Not only is it able to generate texts, but it can also provide answers with images. Only the test version is available for free. A monthly fee is required to use all functions.
Jasper Chat
Jasper Chat is an AI chatbot copywriting tool focused specifically on generating text for businesses that want to create brand-relevant content and have conversations with their customers. Content creators can specify SEO keywords and tone in prompts.
YouChat
YouChat is an AI chatbot for the German-based search engine You.com. YouChat not only provides answers to questions but also provides citations of answers so users can check the source and fact-check You.com’s answers.
NeevaAI
Like YouChat, NeevaAI is part of the German search engine company Neeva. Provide a link to the cited source and use the citation from the original source to generate your answer. You can also summarize multiple sources to provide a single answer.
Summary
To recapitulate, each AI chatbot has its unique selling point, but ChatGPT seems to surpass all its rivals at the time this article was written. However, keep in mind that both models are still in the development stage, and their features will continue to be researched and developed.
Their growth will no doubt make the ChatGPT vs. Google Bard rivalry even more interesting. We are here to give you all the latest information. Please keep watching this blog.
What do you think of this showdown between two AI chatbots? Do you prefer one over the other? Let us know in the comments below.
Relipa has 7 years of experience working as a contractor for Japanese IT companies in the fields of information technology, blockchain, and AI. Aiming for low-cost and efficient offshore development, engineers with excellent English language skills, project managers, and high-quality developers will guarantee quality while conducting “reporting and consultation” 100% in Japanese during the contract period. I promise to